The Distinct Characteristics of the Korean Game Market
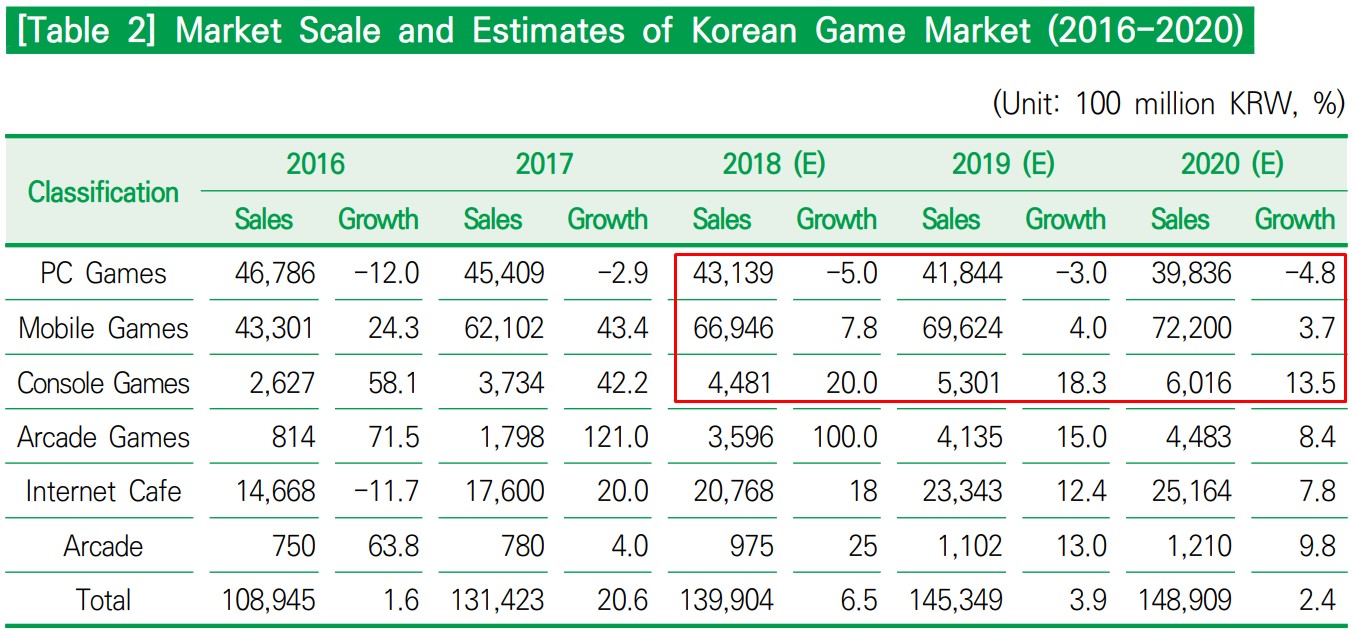
In the global game market, the APAC market is quite significant. In total, the APAC territories generate 51.8% of total global game revenues.
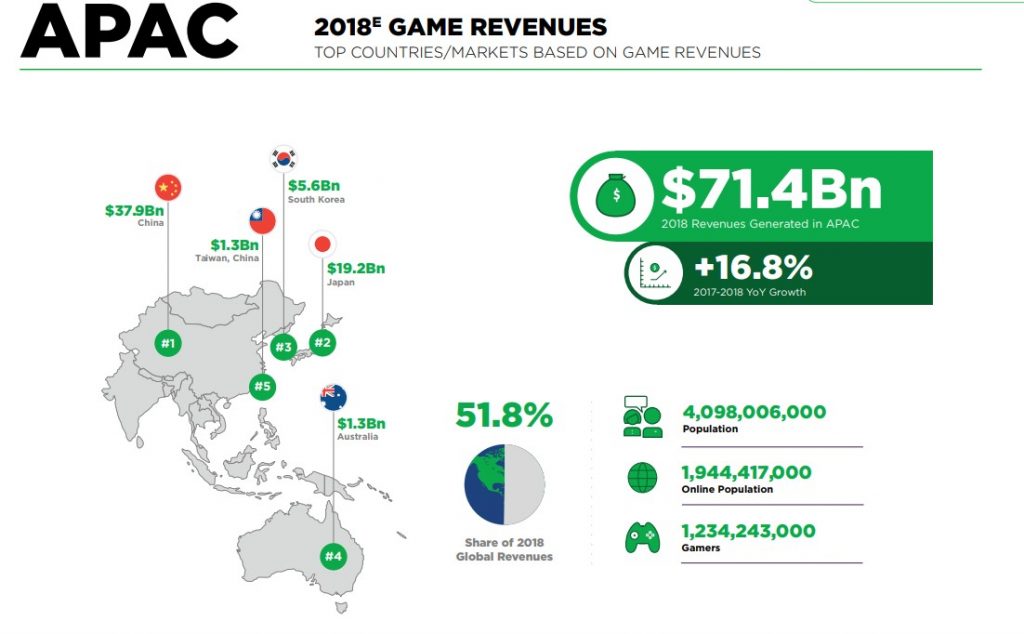
Among them, the Korean game industry is the world’s fourth largest in terms of revenue.
Many game service providers in the US and Europe emphasize how big the APAC region, including the Korean market, and how attractive the market is. However, it is not easy to make a successful foray into the APAC region. This is because large markets such as Korea, China, Japan, and Taiwan have different characteristics, and the appropriate approach varies accordingly.
The Korean game market is certainly a big market among APAC region. However, it’s somewhat inappropriate to use common methods when entering the Korean game market, since many characteristics unique to the Korean market cannot be overlooked. (Typically, the Korean game market is highly focused on PC online games and mobile games.) In this article, we will briefly look at what distinct characteristics the Korean game market has, compared to other markets.
The source of the information below is the 2018 White Paper on Korean Games issued by the Korea Creative Content Agency (KOCCA), a government-affiliated organization.
To download the summary reports in English and Chinese, please check the link below:
1. Composition of the Korean Game Market
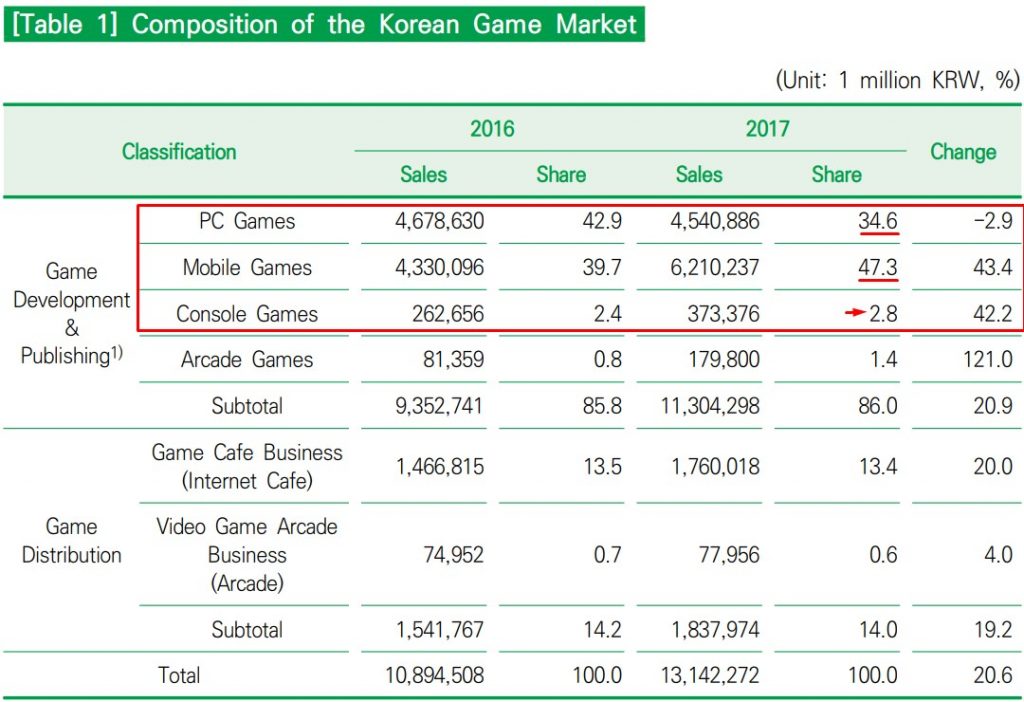
As of 2017, the proportion of PCs and mobile games in the Korean game market is very high. It accounts for 83% of the total. The PC game sector was able to see a remarkable growth thanks to the strong performance of MMORPG games in Korea. The mobile
Therefore, global publishers and developers who play console games as their main business may find the Korean market less marketable than Japanese or Chinese game market. The proportion of console game sector is not as large as in Japan, and it’s difficult to be sure that the Korean game market has unlimited potential as the Chinese market. (But this does not mean that it is relatively easy to enter the Japanese or Chinese market.) However, the recent market trends suggest that the outlook is not as negative as it seems.
2. The Growth Potential of the Korean Console Game Market
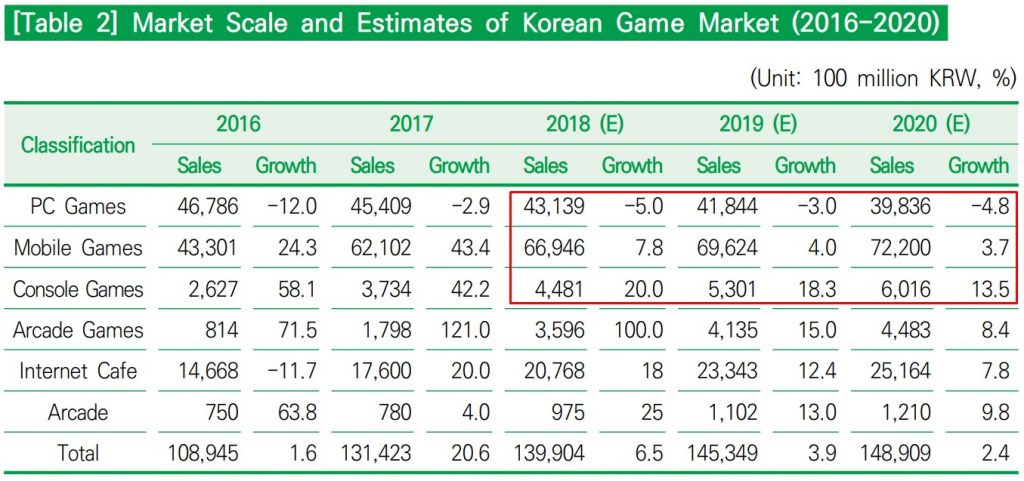
The table above shows the sales and growth trends of the Korean game market by sector. (Figures for 2016 and 2017 are actual amounts, and figures from 2018 to 2020 are estimates.) In the PC game sector, which is already saturated, both sales and growth are declining. The mobile game sector is also likely to see a decrease in growth, as the market has grown so fast. Indeed, in Korea, large domestic publishers have dominated the domestic mobile game market for two or three years with its capital strength. As a result, small and medium-sized publishers tend to downsize their business.
In contrast, the console game sector has been growing steadily over two decades since 2016. This is mainly due to the increase in the traditional console platforms (PS4, Wii, Xbox One) games as well as VR games. In particular, VR and AR are continuously being supported by the Korean government and the number of offline VR game cafés is also on a rise. In addition, game industry insiders say that the console game sector was able to draw users’ attention as there was no MMORPG that meets users’ expectations and they were fed up with mobile games all of a sort.
As a result, some Korean developers, which had released MMORPGs for PC, attempted to release console games by utilizing
3. The Potential Korean Clients for Game Service Providers
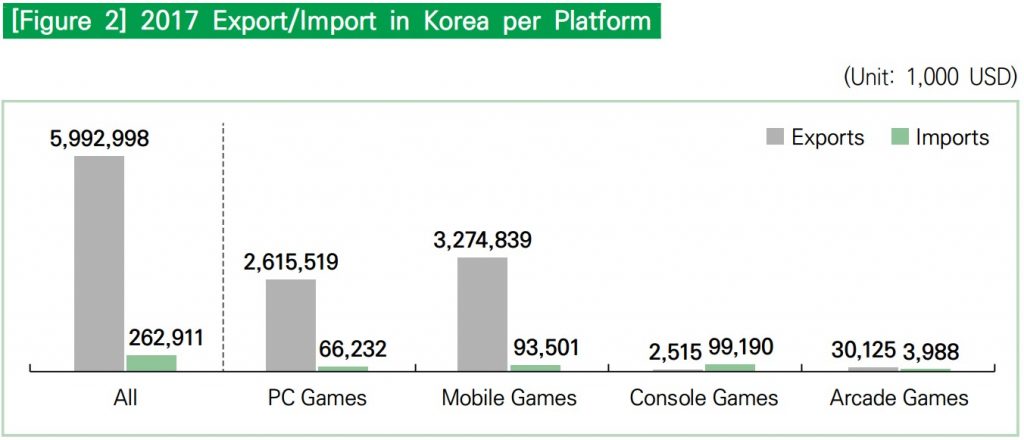
The 2018 White Paper on Korean Game Market notes that the volume of exports and imports of the Korean game market is substantial. Indeed, the amount of exports by Korean publishers and developers has increased year by year, and PC and mobile sales account for more than 10% of global sales.
It also provides the actual indicators for the game service industry. According to the report, there are 888 developers/publishers, 11,349 internet cafés, 700 arcades in Korea. Also, there are 81,932 employees in the game industry.
Looking at these indicators, the Korean market seems very attractive to game service providers. They may think that there are over 900 potential customers who need services when entering the global market.
However, it should not be overlooked that most of the above performance is concentrated on some IP games owned by three large domestic publishers (i.e. Nexon, NC Soft, and Netmarble). For game service providers, the actual number of projects to be carried out may not be large. Most large domestic game publishers already have their own human resources for game services, and overseas branch offices and global networks for overseas service.
The situation of the rest of the game publishers is not so optimistic. As market competition intensifies, medium-sized publishers have been downsizing their business for the past three to four years. A lot of small publishers and developers went out of business for similar reasons.
So far
If you have any questions, please contact us via info@musaikorea.com. BOOST YOUR PLAY! Musai Studio








1 thought on “The Distinct Characteristics of the Korean Game Market”